Ankylosing spondylitis treatment means Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the spine, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Ankylosing spondylitis treatment
It is a form of spondyloarthritis, a group of rheumatic diseases characterized by inflammation in the joints and entheses.
Over the years, advancements in medical research and technology have revolutionized the management of AS, offering patients a more comprehensive and effective range of treatment options.
This article will explore the latest developments in the treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis.
Non-Pharmacological Approaches
Exercise and Physical Therapy
Regular exercise and physical therapy play a crucial role in managing Ankylosing Spondylitis. A well-designed exercise program can improve flexibility, reduce stiffness, and maintain joint function.
Specific exercises that focus on the spine and affected joints help to prevent deformities and maintain posture. Physical therapists tailor exercise plans to each patient’s individual needs and abilities.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Application of heat packs or warm baths can alleviate pain and stiffness by relaxing the muscles and improving blood flow. Conversely, cold packs can help reduce inflammation and swelling in affected areas.
Posture and Body Mechanics
Maintaining good posture and learning proper body mechanics are essential for patients with AS. This can reduce stress on the spine and help prevent further damage.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs are often the first line of pharmacological treatment for AS. They help reduce pain and inflammation, enabling patients to better manage their symptoms and maintain their daily activities.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
DMARDs, such as sulfasalazine and methotrexate, may be prescribed for patients with more severe AS to slow down disease progression and reduce inflammation.
Biologic Therapies
In recent years, biologic therapies have revolutionized AS treatment.
Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) inhibitors, such as etanercept, adalimumab, and infliximab, are biologic drugs that target specific molecules involved in the inflammatory process.
They have shown significant efficacy in reducing symptoms and improving physical function in patients with AS.
Interleukin Inhibitors
Newer biologics that target interleukins, such as secukinumab and ixekizumab, have also demonstrated positive outcomes in AS treatment.

These medications block specific interleukins responsible for inflammation, providing relief to patients who may not respond well to TNF inhibitors.
Surgical Options
In severe cases of AS where joint damage is irreversible or spinal deformities lead to significant disability, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Surgical procedures such as joint replacement (e.g., hip or knee) and spinal fusion can improve function, relieve pain, and correct deformities.
Emerging Therapies
Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitors
JAK inhibitors are a newer class of drugs that target the JAK signaling pathway involved in the immune response.
Early studies suggest that JAK inhibitors may have potential in treating AS, offering patients another promising treatment option.
Stem Cell Therapy
While still in its early stages, stem cell therapy holds promise for regenerating damaged tissues and reducing inflammation in AS.
Research in this area is ongoing, and clinical trials are being conducted to explore the safety and efficacy of stem cell treatments.
Ankylosing spondylitis treatment
Ankylosing Spondylitis treatment has come a long way, with significant advancements in both non-pharmacological and pharmacological approaches.
Regular exercise, physical therapy, and maintaining good posture remain fundamental in managing AS symptoms.
Pharmacological treatments, especially biologic therapies, have revolutionized the management of the disease, providing relief and improved quality of life for many patients.
As research continues, emerging therapies and potential breakthroughs offer hope for even better outcomes in the future. Early diagnosis, appropriate treatment. A multidisciplinary approach are key to effectively managing Ankylosing Spondylitis and improving the lives of those affected by this challenging condition.
Lifestyle Considerations
Smoking Cessation
Smoking has been linked to increased disease activity and progression in AS. Quitting smoking can significantly improve treatment outcomes and reduce the severity of symptoms.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for AS patients, as excess weight can put additional stress on the spine and joints. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help manage weight and improve overall health.
Sleep Quality
Proper sleep is crucial for managing pain and fatigue associated with AS. Investing in a comfortable mattress and adopting good sleep hygiene practices can promote better sleep quality.
Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate inflammation and contribute to symptom flare-ups. Employing stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga can be beneficial for patients with AS.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Acupuncture
Acupuncture, an ancient Chinese therapy, involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow. Some AS patients have reported reduced pain and improved mobility with acupuncture sessions.
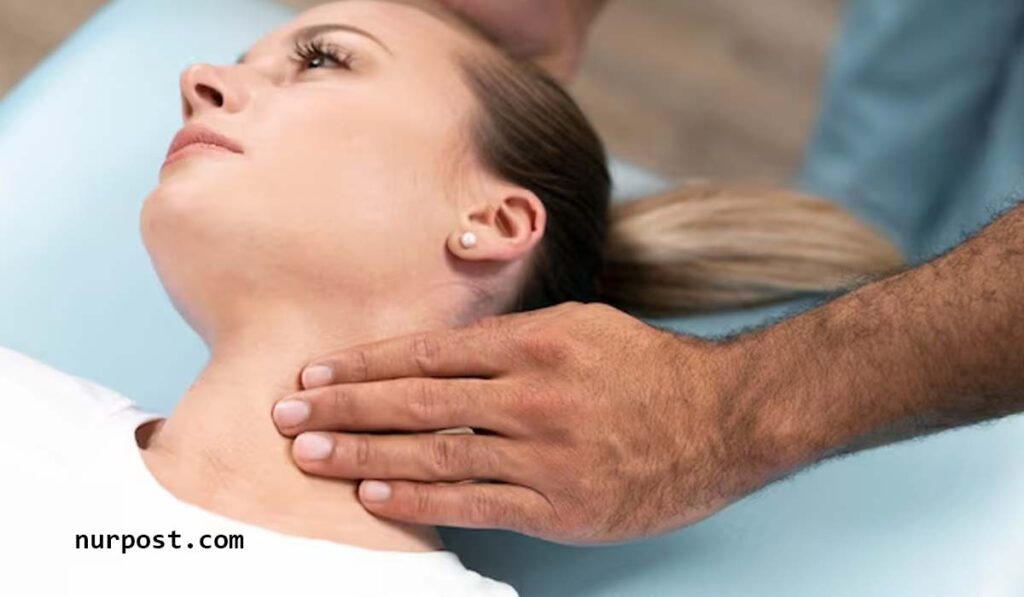
Massage Therapy
Massage therapy can help relax muscles, reduce pain, and improve joint mobility in AS patients. It is often used as a complementary treatment alongside conventional medical therapies.
Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic adjustments may provide relief for some AS patients by improving spinal alignment and joint function.
However, it is essential to work with a chiropractor experienced in treating AS to avoid potential complications.
Patient Education and Support
Educating patients about their condition and empowering them to be proactive in their treatment are vital aspects of AS management.
Support groups and online forums provide valuable platforms for patients to connect with others facing similar challenges, share experiences, and gain emotional support.
Monitoring and Regular Check-ups
Regular follow-ups with rheumatologists are crucial for monitoring disease progression, assessing treatment efficacy, and making necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Routine check-ups can also help identify any potential complications early on.
Individualized Treatment Plans
Ankylosing Spondylitis is a complex disease, and its impact can vary significantly from person to person. Tailoring treatment plans to each patient’s specific needs and symptoms is essential for optimal outcomes.
Rheumatologists work closely with patients to develop personalized treatment strategies.
Conclusion
Ankylosing Spondylitis treatment has evolved significantly over the years, providing patients with a range of options to manage their condition effectively.
From non-pharmacological approaches like exercise and physical therapy to pharmacological treatments.
Such as biologic therapies and emerging treatments like JAK inhibitors and stem cell therapy, the landscape of AS treatment is continually expanding.
Ankylosing spondylitis treatment
It is essential to remember that AS is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management.
A comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, appropriate medication, and regular medical check-ups can enable patients to lead fulfilling lives with minimized symptoms and improved mobility.
As research and medical advancements continue, the future holds promise for even more innovative and effective treatments for Ankylosing Spondylitis.